| Botanic name | Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ |
| Other names | Dwarf Yellow Bloodwood |
| Main Origin | Central coastal and subcoastal New South Wales |
| Mature size | 5 m x 6 – 8 m (w x h) |
| Mature form | Compact with a rounded, dense, or slightly open canopy |
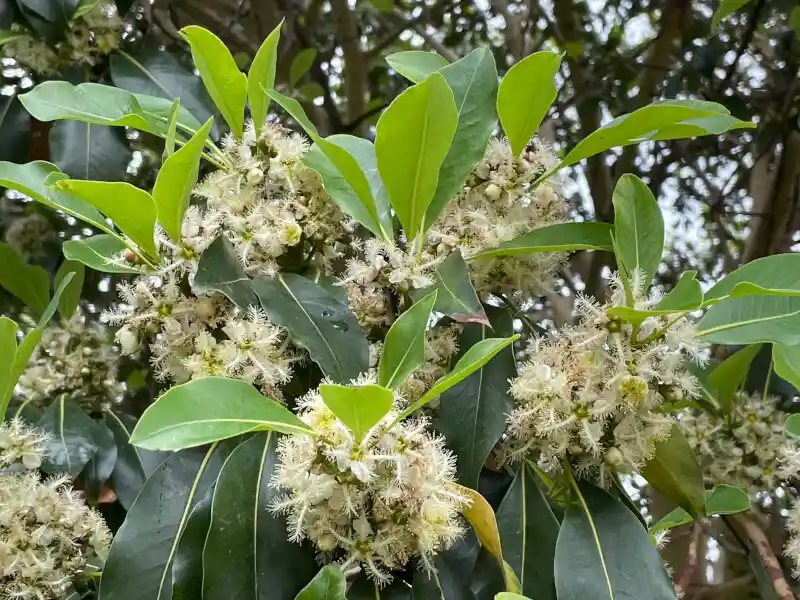
| Foliage | Spear- or sickle-shaped, greyish-green |
| Growth rate | Moderate |
| Position | Full sun |
| Soil | Adaptable to most well-drained soils |
| Water | Occasional deep watering during hot & dry periods |
| Climate | Subtropical, warm temperate, and Mediterranean |
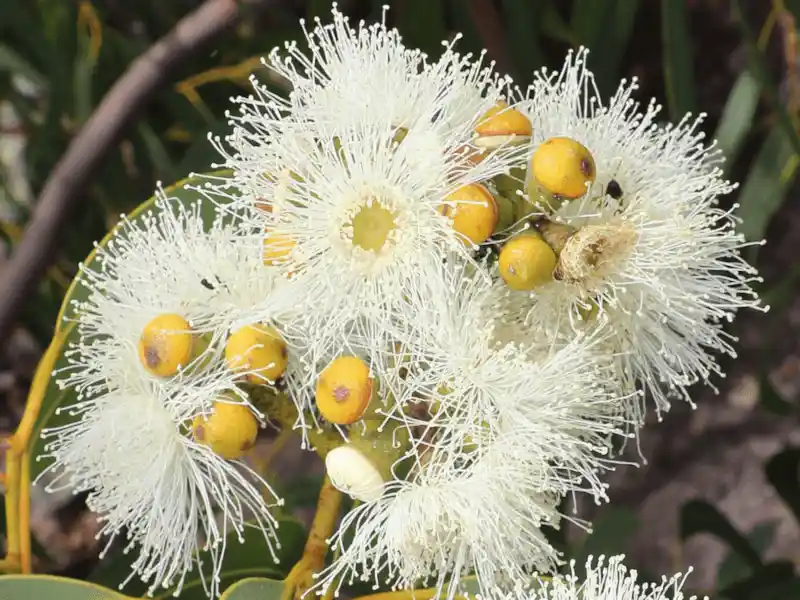
| Flower | Creamy white from late winter to spring |
| Use | Feature tree, shade tree, windbreak, avenue planting |
| Notes | Suitable for coastal sites |
IN THIS ARTICLE
Overview
People who know Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ (Dwarf Yellow Bloodwood) love its striking features, including its bold foliage, gnarled trunk, tessellated flaky bark, and prolific creamy white flowers.
Because of its strong presence in a compact form, Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ is highly popular in streetscapes and parklands.
This article will explore this fascinating tree and its distinctive traits inherited from Corymbia eximia. Let’s look at its unique attributes and suitability for smaller gardens.

Corymbia eximia (Yellow Bloodwood)
Corymbia eximia, or Yellow Bloodwood, is a medium-sized tree endemic to coastal and subcoastal regions around Sydney, Australia. It mainly thrives in dry forests on sandstone soils.
Yellow Bloodwood is well-adapted to the fire-prone areas and can regenerate from dormant buds after bushfires. It is drought-tolerant and can withstand light to moderate frost. It prefers well-drained soils and full sun exposure.
The tree’s greyish-green, spear-shaped leaves are thick and veiny and can measure 20 – 24 cm long. This contributes significantly to its prominent impression on the landscape. The foliage often turns paler in cooler months.
Corymbia exima typically reaches up to 20 metres in height and is characterised by its distinctive yellow-brown, flaky, tessellated bark. The gnarly, mottled wood, combined with the tree’s crooked trunk, adds significant visual interest to the tree.
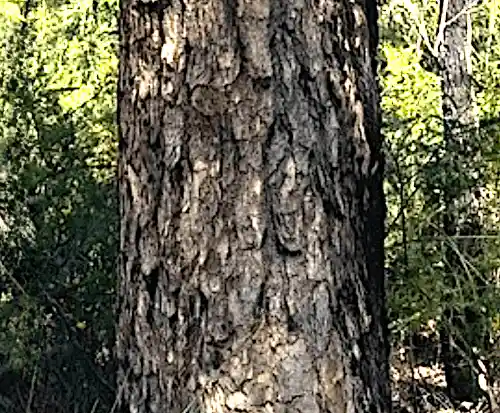

Corymbia eximia has a spreading habit with a dome-shaped canopy that forms a neat appearance. From late winter to spring, it produces large cream-colored flowers arranged in clusters of seven at the branch terminals, attracting native birds and bees.
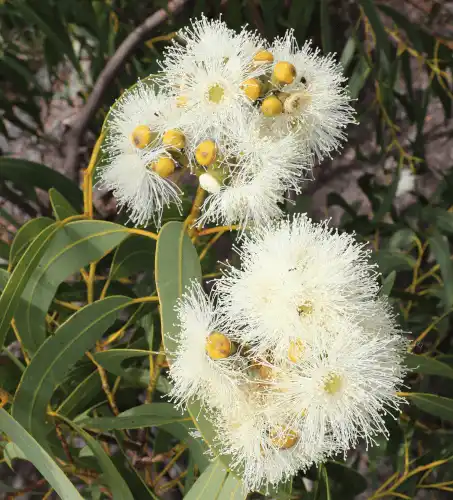

Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ (Dwarf Yellow Bloodwood)
Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ is a dwarf cultivar of Yellow Bloodwood, growing to approximately 6 to 8 meters. This smaller variety shares nearly all features with its parent species, including the gnarly trunk and broad, long green leaves that may turn a pale yellow-green in colder months.
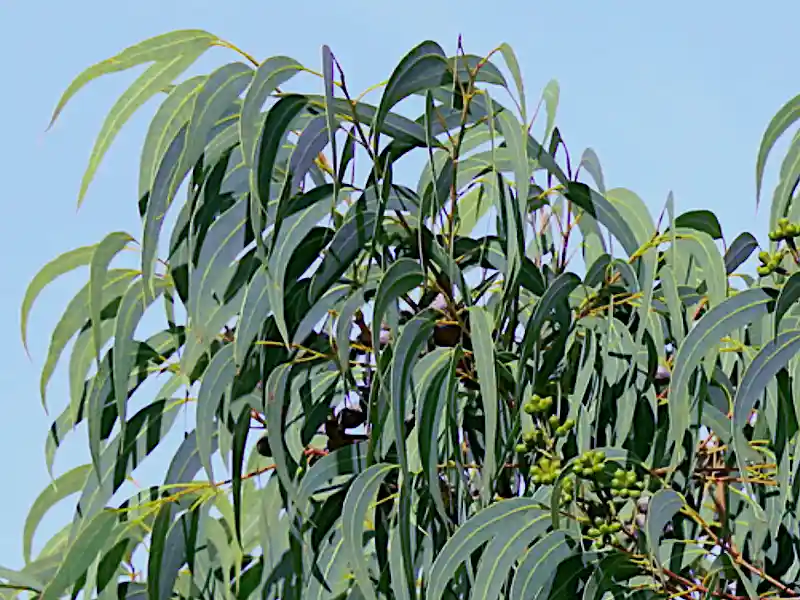

However, a compact size makes it more suitable for smaller gardens and urban landscapes. While the standard Corymbia eximia is ideal for larger spaces, the ‘Nana’ cultivar offers the same ornamental appeal in a much more manageable form.
Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ is celebrated not only for its compact, striking appearance but also for its exceptional longevity. Adapted to thrive in challenging environments, this Dwarf Yellow Bloodwood is remarkably hardy, capable of flourishing for many decades in the right conditions.
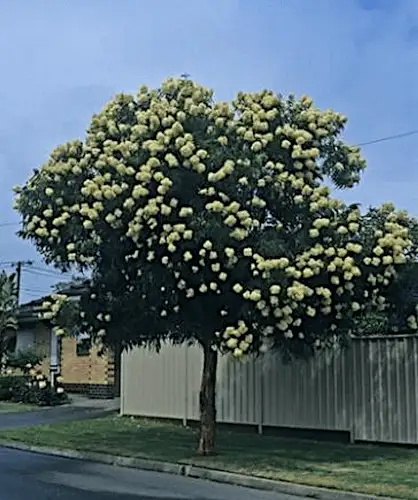

Its robust genetic makeup, resilience in nutrient-poor soils, and tolerance for drought and moderate frost ensure it will endure the test of time. For gardeners seeking a lasting investment in natural beauty, Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’ stands as a living legacy that will add charm and resilience to landscapes for many generations.
FAQs
How big does Dwarf Yellow Bloodwood get?
At maturity, Dwarf Yellow Bloodwood (Corymbia eximia ‘Nana’) can reach 6 – 8 metres tall, making it ideal for small gardens or planting spaces where the tree height is a concern.
How long do bloodwood trees live?
Bloodwood trees, including notable species like the Yellow Bloodwood (Corymbia eximia) and Red Bloodwood (Corymbia gummifera), are renowned for their longevity. Under favourable conditions, they can live well over 100 years.
Is bloodwood a eucalypt?
Yes, bloodwood trees are indeed eucalypts. Bloodwood trees belong to the Corymbia family, which produces red sap and richly coloured heartwood. Corymbia is part of the eucalypt group.


